Molar Extraction In A Dog
Molar 1 extraction in a dog.
The First molar in the bottom or mandibular molar 1 – is the largest tooth in the jaw bone of a dog. In a staffie the tooth is massive and needs a 1 hour surgical extraction by the canine dentist.
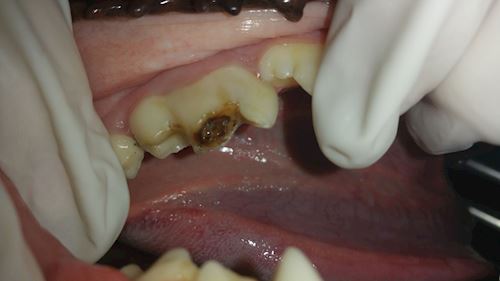
Above: Note how large the tooth is – and the large “Pus pocket” filling the middle of the tooth. Being a carnivore the dogs teeth are well rooted. They can not be pulled out !! The veterinary dentist needs to loosen the roots first.
They need a veterinary dental surgical extraction!
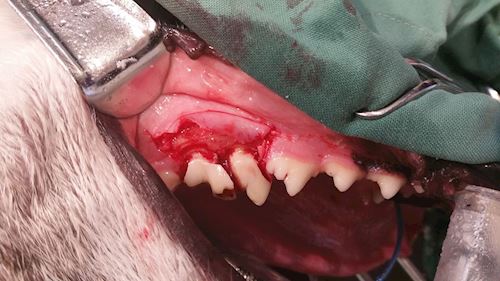
Above: A gum flap is made and the tooth is gently sectioned while the pet is under light anesthesia – the root canal or pulp cavity was filled with infected material – and this was not a candidate for a root canal by a specialist veterinary dentist.
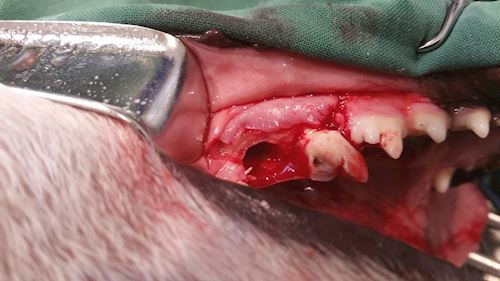
Above: The tooth has been sectioned in half and half the tooth with its root has been removed. Note the large root cavity. The remaining half is gently extracted , the root cavity cleaned and flushed – and then closure
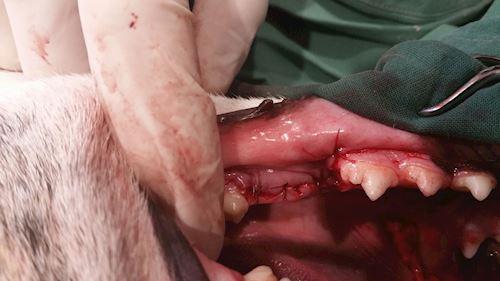
Above: Finally the dog dentist closed the gum flap using a thin rapidly absorbable suture.
Mischa the 7.5 year old patient – made a rapid recovery – as expected from the veterinary dental anesthetic. Mischa went home on a course of antibiotics and was given a 2 day anti- inflammatory – pain relief injection
Why does my dog/cat need his or her teeth cleaned and evaluated?
Just like you and I, veterinary dental care is important for the overall health of your dog. Dogs benefit from daily at home dental care. . Dental disease is present in 80% of dogs and 70% of cats by three years of age. Small breed dogs in particular can develop periodontal disease early in life.
Advanced ongoing dental disease leads to disease in the heart, liver, or kidneys from bacteria entering the blood stream . Dog dental disease can cause anemia due to chronic disease. It can unwell and cause considerable dental pain. Many pets have enough dental disease affect their attitude and ability to play and live normally . Dental disease can lead to tooth loss, gum infection, tooth root abscesses, and oral pain.
